Neural and behavioural predictors of anxiety in young children
Last updated on
Jan 29, 2025
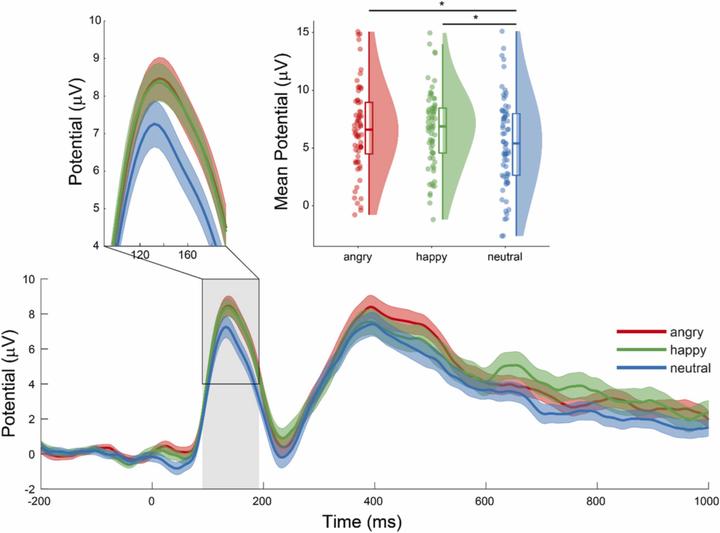
Developmental EEG and eye-tracking research focused on how affect-biased attention and behavioural inhibition influence the risk for anxiety in early childhood.
EEG
ERP
child
facial expression
emotion
affect-biased attention
anxiety
behavioral inhibition
longitudinal
gaze
eye-tracking
Related
- Behavioural inhibition and early neural processing of happy and angry faces interact to predict anxiety: a longitudinal ERP study
- Trajectories of anxiety when children start school: The role of behavioral inhibition and attention bias to angry and happy faces
- Early social adversity modulates the relation between attention biases and socioemotional behaviour in juvenile macaques
- Mu desynchronization during observation and execution of facial expressions in 30-month-old children
- Early maternal mirroring predicts infant motor system activation during facial expression observation
Publications
Intolerance of uncertainty (IU) is the tendency to find uncertainty distressing. IU is related to anxiety in adults and youth but it is …
Zoe J Ryan,
Holly Rayson,
Jayne Morriss,
Helen F Dodd
Limited prospective research has examined whether attention biases to emotion moderate associations between Behavioural Inhibition (BI) …
Holly Rayson,
Zoe J Ryan,
Helen F Dodd
Extensive research has examined attention bias to threat in the context of anxiety in adults, but little is understood about this …
Helen F Dodd,
Holly Rayson,
Zoe Ryan,
Corinne Bishop,
Sam Parsons,
Bobby Stuijfzand